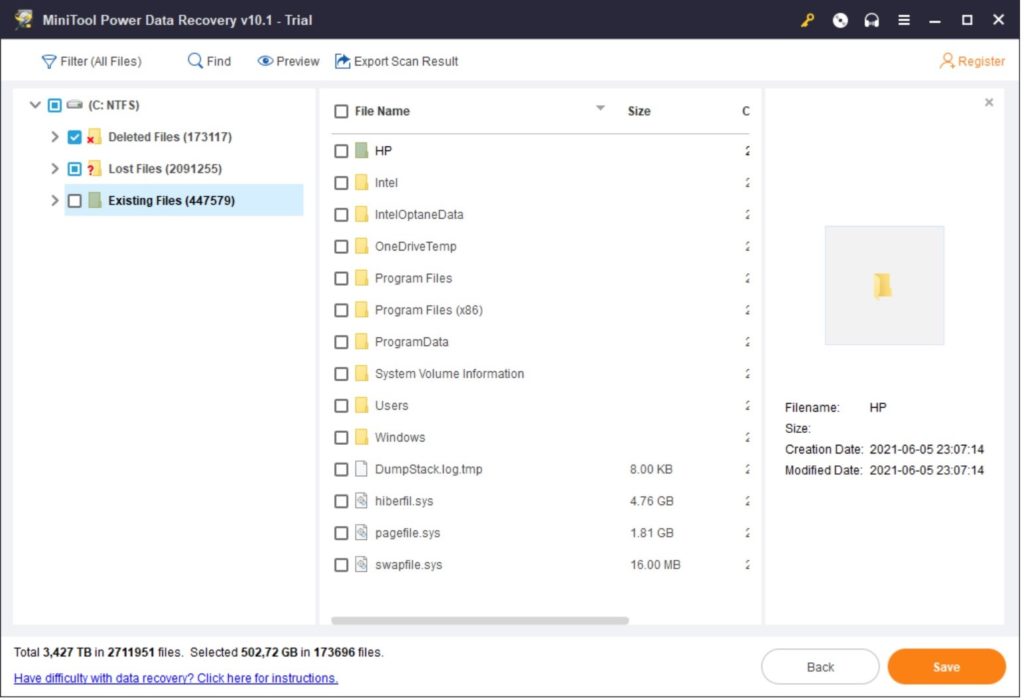
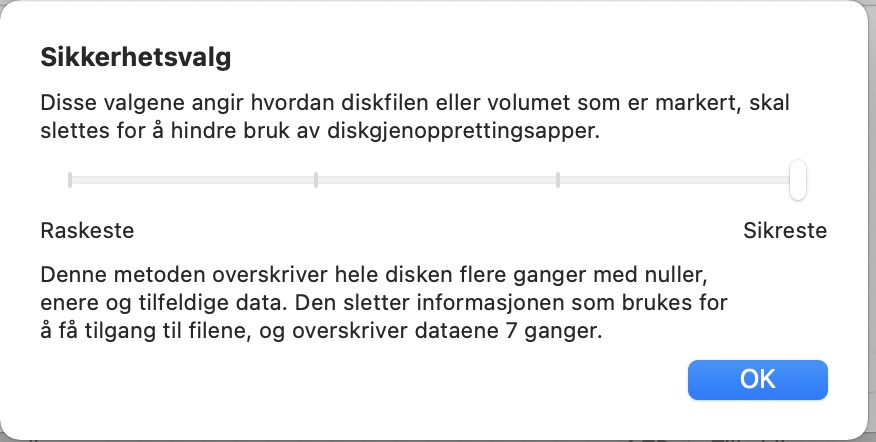
Det er mulig å forlenge Mac maskiners levetid ved å tvinge inn et nytt operativsystem på dem mot Apples råd og godkjenning. Det gjøres ved så kalt core patching eller operativsystem-manipulering. Noen i flere åpen kildekode-miljøer har laget ulike systemer for å redigere oppstarts-sekvensene og operativsystemene på en Mac maskin og så få en gammel maskin til å fungere med et nytt operativsystem som Apple ikke godkjenner eller har anbefalt. En av dem er Open Core Legacy Patcher eller OCLP. Jeg har prøvet det her hjemme på en iMac 2013 og fikk inn macOS Sonoma på den som er Apples nest siste versjon av macOS. Det måtte lages en oppstarts-usb-stikk fra opencore installasjonen på en annen maskin og så ble det patchede eller tilpassede systemet installert på en eldre maskin fra 2013 som Apple ikke sa det skulle passe på.
Resultat: macOS Sonoma kom inn på maskinen og fungerte men etter hver oppdatering av operativsystemet fra Apple sin side måtte eieren av maskinen også oppdatere root-patching via opencore appen på maskinen. Det førte til at oppdateringen fra Apple ikke alltid kom inn før etter flere forsøk og etter hver oppdatering fra Apple måtte brukeren selv oppdatere root-patchingen selv som tar litt tid. Da hendte det også at ikke all patchingen gikk i orden og måtte utføres flere ganger.
Hovedinnvendingen mot dette systemet er at det er litt tungvint å få installert og litt tungvint å bruke, men den vektigste innvendingen er om de som gratis sørger for disse patche-systemene har nok økonomi og egeninteresse i å holde systemene sikre siden de ikke tjener noe på dem. Det har jeg ikke svar på. Når det gjelder Apples og Microsoft sine systemer så er det nokså sannsynlig at med tap av milliarder av dollar hvis de ikke holder systemene sikre så antar jeg at det er nokså nært 100 % sikkert å bruke de originale operativsystemene slik produsenten ber om!!
It is possible to extend the life of Macs by forcing a new operating system on them against Apple’s advice and approval. This is done through what is called core patching or operating system manipulation. Some people in several open source communities have created various systems to edit the boot sequences and operating systems on a Mac and then make an old machine work with a new operating system that Apple does not approve or recommend. One of them is the Open Core Legacy Patcher or OCLP. I have tried it here at home on a 2013 iMac and got macOS Sonoma on it, which is Apple’s second-to-last version of macOS. A bootable USB stick had to be made from the opencore installation on another machine and then the patched or customized system was installed on an older machine from 2013 that Apple did not say it would be compatible with.
Result: macOS Sonoma came onto the machine and worked, but after each update of the operating system from Apple, the owner of the machine also had to update the root patching via the opencore app on the machine. This meant that the update from Apple did not always arrive until after several attempts, and after each update from Apple, the user had to update the root patching themselves, which takes some time. Then it also happened that not all the patching went well and had to be done several times.
The main objection to this system is that it is a bit cumbersome to install and a bit cumbersome to use, but the most important objection is whether those who provide these matching systems for free have enough finances and self-interest in keeping the systems secure since they do not make any money from them. I do not have an answer to that. When it comes to Apple’s and Microsoft’s systems, it is quite likely that with losses of billions of dollars if they do not keep the systems secure, I assume that it is quite close to 100% safe to use the original operating systems as the manufacturer requests!!